Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR): HIRS
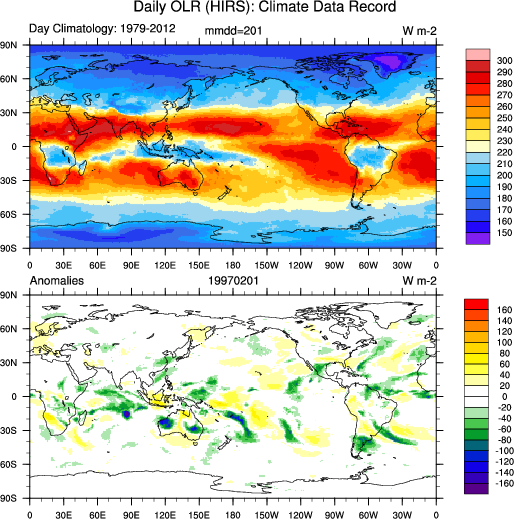
"The new Climate Data Record (CDR) provides daily global climate data that are valuable as inputs into Radiation Budget Studies and verifying numerical models and can identify the variations in tropical clouds and rainfall that drive global weather patterns. The daily climate data of OLR can provide radiance observations at a 1.0x1.0 Degree resolution, creating aconsistent long term climate record of observations since 1979 .
Developed by NOAA and the University of Maryland, the OLR – Daily CDR data are derived from the High Resolution Infrared Radiation Sounder (HIRS) instruments on board NOAA TIROS-N series and Eumetsat MetOp polar orbiting satellites, and the legacy and present day Imager instruments on board the multinational operational geostationary satellites. This product will be extended with the new generations of operational sounding instruments on board Suomi‐NPP, JPSS, MetOp, etc., and imaging instruments on board geostationary satellites." [http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/cdr/operationalcdrs.html#2]
"The product contains the 1-degree by 1-degree daily mean outgoing longwave radiation flux at the top of the atmosphere derived from HIRS radiance observations onboard NOAA TIROS-N series and MetOp satellites. The OLR retrieval uses multispectral regression models (Ellingson et al., 1989, Lee, 2014). The CDR processing includes HIRS radiance calibration, inter-satellite HIRS OLR calibration, normalization of geostationary-based OLR retrieval to HIRS, and grid-based 7-day boxcar temporal integration assisted with Imager-based OLR derived from Gridsat CDR data (Lee, 2014)."
OLR (Outgoing Longwave Radiation) is a measure of the amount of energy emitted to space by earth's surface, oceans and atmosphere. As such, it is a critical component of the earth's radiation budget. In a different context, OLR values are often used as a proxy for convection in tropical and subtropical regions since cloud top temperatures (colder is higher) are an indicator of cloud height.
OLR estimates are a key component for the standard Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) CLIVAR diagnostics which are used to study the MJO and for climate model evaluation.
Key Strengths
Climate Data Record: Here, a time series of spatial OLR measurements since 1979 .
1x1 high resolution
Cite this page
Acknowledgement of any material taken from or knowledge gained from this page is appreciated:
National Center for Atmospheric Research Staff (Eds). Last modified "The Climate Data Guide: Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR): HIRS.” Retrieved from https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/outgoing-longwave-radiation-olr-hirs on 2025-04-09.
Citation of datasets is separate and should be done according to the data providers' instructions. If known to us, data citation instructions are given in the Data Access section, above.
Acknowledgement of the Climate Data Guide project is also appreciated:
Schneider, D. P., C. Deser, J. Fasullo, and K. E. Trenberth, 2013: Climate Data Guide Spurs Discovery and Understanding. Eos Trans. AGU, 94, 121–122, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013eo130001
Key Figures
Other Information
1 x 1 (daily)
,2.5 x 2.5 (monthly)
- Emma C. Turner, Simon F. B. Tett. (2014) Using longwave HIRS radiances to test climate models. Climate Dynamics 43, 1103-1127
- Hai-Tien Lee, et al, 2007: Development of the HIRS Outgoing Longwave Radiation Climate Dataset. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 24, 2029–2047
- Lee HT, Ellingson RG (2013) HIRS OLR climate data record–production and validation updates. In: AIP conference proceedings, vol 1531, p 420
- Ellingson,R.G. et al (1994): Validation of a Technique for Estimating Outgoing Longwave Radiation from HIRS Radiance Observations. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 11, 357–365

